サービス工学分野
Optimizing the Strategic Decisions for One-way Station-based Carsharing Systems: A Mean-CVaR Approach
プロジェクトメンバー
- Kai ZHANG Kai ZHANG
システム情報工学研究群 社会工学学位プログラム - 高野 祐一 Yuichi TAKANO
システム情報系/人工知能科学センター(サービス工学分野) - Yuzhu WANG Yuzhu WANG
システム情報工学研究群 社会工学学位プログラム - 吉瀬 章子 Akiko YOSHISE
システム情報系/人工知能科学センター(サービス工学分野)
研究概要
Background
Mobility as a Service (MaaS)
- build a seamless and integrated multimodal mobility system.
- promote some emerging mobility services, such as carsharing.
Emerging Carsharing Services (Figure 1)
- provide a potential solution to first- or last-mile problems.
Society 5.0 in Japan
- make movement smooth by combining carsharing services, public transportation.
Our Research
Focus on one-way station-based carsharing systems.
- One-way trips usually occupy a large proportion of trips.
- Operators can manage vehicles more easily.
Present a two-stage risk-averse model.
- Risk measure: Conditional Value-at-Risk (CVaR) (Figure 2)
- Strategic decisions: station locations, station size and fleet size
Develop two algorithms to solve the problem.
- Branch-and-cut: handle the nonlinear CVaR function.
- Scenario decomposition: handle the special block-angular structure of the problem.
Conduct the experiments based on the data from Ha:mo RIDE, Toyota.
Experimental Results
- Efficient frontiers of mean return and conditional value-at-risk (CVaR) for different confidence levels β (Figure 3)
- Optimal station locations and capacities for different weights λ between return and risk (Figure 4)

Figure 1: Toyota Ha:mo RIDE carsharing, Japan
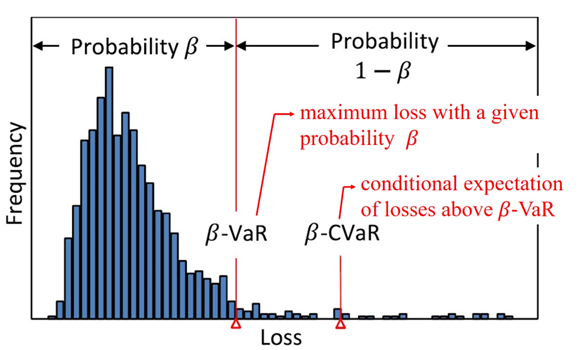
Figure 2: Value-at-Risk (VaR) and Conditional Value-at-Risk (CVaR)
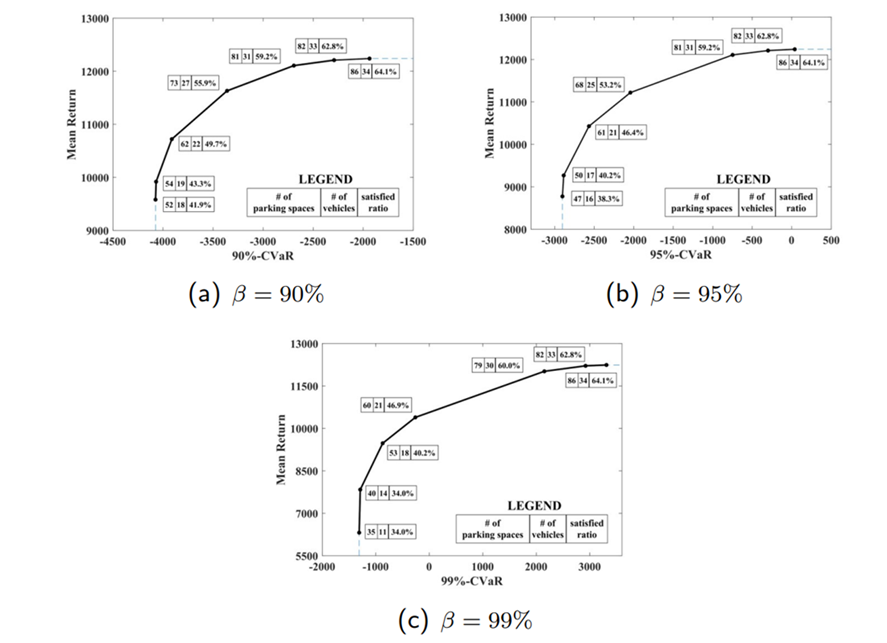
Figure 3: Efficient frontiers of mean return and conditional value-at-risk (CVaR) for different confidence levels β
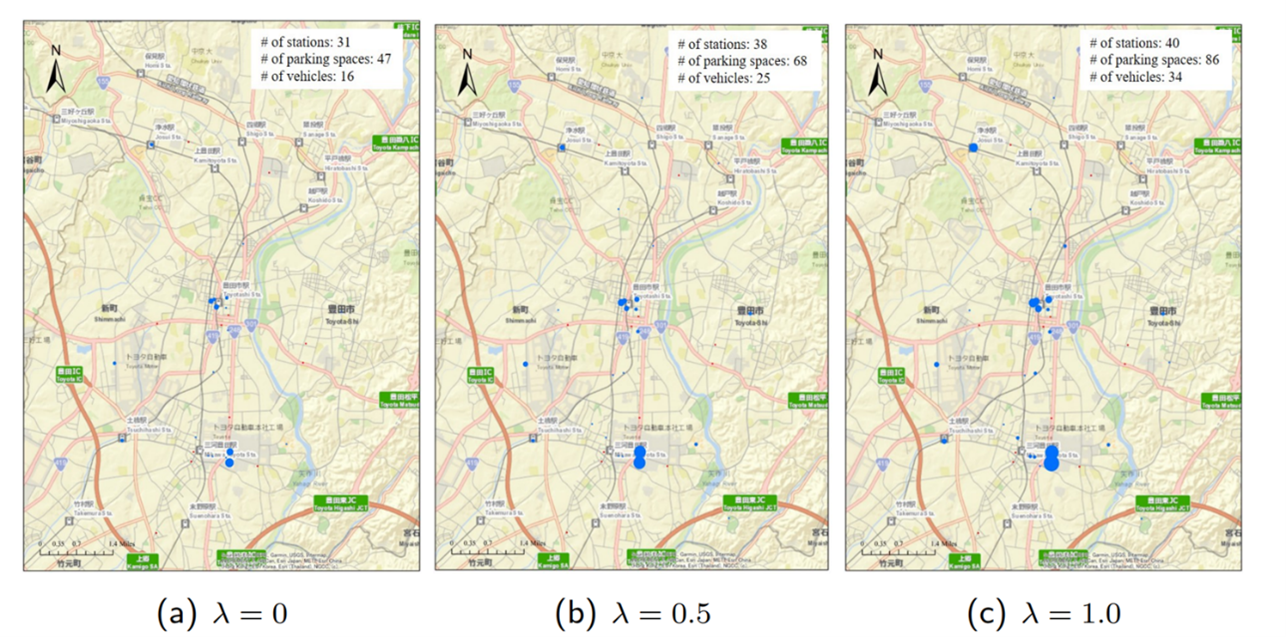
Figure 4: Optimal station locations and capacities for different weights λ between return and risk
参考文献
[1] Zhang, K., Takano, Y., Wang, Y., & Yoshise, A. (2021). Optimizing the strategic decisions for one-way station-based carsharing systems: A mean-CVaR approach. IEEE Access, 9, 79816-79828.